mirror of
https://github.com/Snailclimb/JavaGuide
synced 2025-08-01 16:28:03 +08:00
Compare commits
6 Commits
2271678f14
...
0574285032
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
0574285032 | ||
|
|
e1e809c9d7 | ||
|
|
b5491ffb35 | ||
|
|
6232dd3f14 | ||
|
|
4f87ee846e | ||
|
|
47df1a878b |
@ -34,6 +34,7 @@ export const highQualityTechnicalArticles = arraySidebar([
|
|||||||
prefix: "programmer/",
|
prefix: "programmer/",
|
||||||
collapsible: false,
|
collapsible: false,
|
||||||
children: [
|
children: [
|
||||||
|
"high-value-certifications-for-programmers",
|
||||||
"how-do-programmers-publish-a-technical-book",
|
"how-do-programmers-publish-a-technical-book",
|
||||||
"efficient-book-publishing-and-practice-guide",
|
"efficient-book-publishing-and-practice-guide",
|
||||||
],
|
],
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -48,14 +48,14 @@ export default hopeTheme({
|
|||||||
notice: [
|
notice: [
|
||||||
{
|
{
|
||||||
path: "/",
|
path: "/",
|
||||||
title: "知识星球",
|
title: "PDF面试资料(2024版)",
|
||||||
showOnce: true,
|
showOnce: true,
|
||||||
content:
|
content:
|
||||||
"专属面试小册/一对一交流/简历修改/专属求职指南,欢迎加入 JavaGuide 知识星球。",
|
"2024最新版原创PDF面试资料来啦!涵盖 Java 核心、数据库、缓存、分布式、设计模式、智力题等内容,非常全面!",
|
||||||
actions: [
|
actions: [
|
||||||
{
|
{
|
||||||
text: "前往了解",
|
text: "点击领取",
|
||||||
link: "https://javaguide.cn/about-the-author/zhishixingqiu-two-years.html",
|
link: "https://oss.javaguide.cn/backend-notekbook/official-account-traffic-backend-notebook-with-data-screenshot.png",
|
||||||
type: "primary",
|
type: "primary",
|
||||||
},
|
},
|
||||||
],
|
],
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -94,7 +94,7 @@ tag:
|
|||||||
- **ARP(Address Resolution Protocol,地址解析协议)**:ARP 协议解决的是网络层地址和链路层地址之间的转换问题。因为一个 IP 数据报在物理上传输的过程中,总是需要知道下一跳(物理上的下一个目的地)该去往何处,但 IP 地址属于逻辑地址,而 MAC 地址才是物理地址,ARP 协议解决了 IP 地址转 MAC 地址的一些问题。
|
- **ARP(Address Resolution Protocol,地址解析协议)**:ARP 协议解决的是网络层地址和链路层地址之间的转换问题。因为一个 IP 数据报在物理上传输的过程中,总是需要知道下一跳(物理上的下一个目的地)该去往何处,但 IP 地址属于逻辑地址,而 MAC 地址才是物理地址,ARP 协议解决了 IP 地址转 MAC 地址的一些问题。
|
||||||
- **ICMP(Internet Control Message Protocol,互联网控制报文协议)**:一种用于传输网络状态和错误消息的协议,常用于网络诊断和故障排除。例如,Ping 工具就使用了 ICMP 协议来测试网络连通性。
|
- **ICMP(Internet Control Message Protocol,互联网控制报文协议)**:一种用于传输网络状态和错误消息的协议,常用于网络诊断和故障排除。例如,Ping 工具就使用了 ICMP 协议来测试网络连通性。
|
||||||
- **NAT(Network Address Translation,网络地址转换协议)**:NAT 协议的应用场景如同它的名称——网络地址转换,应用于内部网到外部网的地址转换过程中。具体地说,在一个小的子网(局域网,LAN)内,各主机使用的是同一个 LAN 下的 IP 地址,但在该 LAN 以外,在广域网(WAN)中,需要一个统一的 IP 地址来标识该 LAN 在整个 Internet 上的位置。
|
- **NAT(Network Address Translation,网络地址转换协议)**:NAT 协议的应用场景如同它的名称——网络地址转换,应用于内部网到外部网的地址转换过程中。具体地说,在一个小的子网(局域网,LAN)内,各主机使用的是同一个 LAN 下的 IP 地址,但在该 LAN 以外,在广域网(WAN)中,需要一个统一的 IP 地址来标识该 LAN 在整个 Internet 上的位置。
|
||||||
- **OSPF(Open Shortest Path First,开放式最短路径优先)** ):一种内部网关协议(Interior Gateway Protocol,IGP),也是广泛使用的一种动态路由协议,基于链路状态算法,考虑了链路的带宽、延迟等因素来选择最佳路径。
|
- **OSPF(Open Shortest Path First,开放式最短路径优先)**:一种内部网关协议(Interior Gateway Protocol,IGP),也是广泛使用的一种动态路由协议,基于链路状态算法,考虑了链路的带宽、延迟等因素来选择最佳路径。
|
||||||
- **RIP(Routing Information Protocol,路由信息协议)**:一种内部网关协议(Interior Gateway Protocol,IGP),也是一种动态路由协议,基于距离向量算法,使用固定的跳数作为度量标准,选择跳数最少的路径作为最佳路径。
|
- **RIP(Routing Information Protocol,路由信息协议)**:一种内部网关协议(Interior Gateway Protocol,IGP),也是一种动态路由协议,基于距离向量算法,使用固定的跳数作为度量标准,选择跳数最少的路径作为最佳路径。
|
||||||
- **BGP(Border Gateway Protocol,边界网关协议)**:一种用来在路由选择域之间交换网络层可达性信息(Network Layer Reachability Information,NLRI)的路由选择协议,具有高度的灵活性和可扩展性。
|
- **BGP(Border Gateway Protocol,边界网关协议)**:一种用来在路由选择域之间交换网络层可达性信息(Network Layer Reachability Information,NLRI)的路由选择协议,具有高度的灵活性和可扩展性。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -216,9 +216,9 @@ WHERE info.exam_id = record.exam_id
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
| total_pv | complete_pv | complete_exam_cnt |
|
| total_pv | complete_pv | complete_exam_cnt |
|
||||||
| -------- | ----------- | ----------------- |
|
| -------- | ----------- | ----------------- |
|
||||||
| 11 | 7 | 2 |
|
| 10 | 7 | 2 |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
解释:表示截止当前,有 11 次试卷作答记录,已完成的作答次数为 7 次(中途退出的为未完成状态,其交卷时间和份数为 NULL),已完成的试卷有 9001 和 9002 两份。
|
解释:表示截止当前,有 10 次试卷作答记录,已完成的作答次数为 7 次(中途退出的为未完成状态,其交卷时间和份数为 NULL),已完成的试卷有 9001 和 9002 两份。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**思路**: 这题一看到统计次数,肯定第一时间就要想到用`COUNT`这个函数来解决,问题是要统计不同的记录,该怎么来写?使用子查询就能解决这个题目(这题用 case when 也能写出来,解法类似,逻辑不同而已);首先在做这个题之前,让我们先来了解一下`COUNT`的基本用法;
|
**思路**: 这题一看到统计次数,肯定第一时间就要想到用`COUNT`这个函数来解决,问题是要统计不同的记录,该怎么来写?使用子查询就能解决这个题目(这题用 case when 也能写出来,解法类似,逻辑不同而已);首先在做这个题之前,让我们先来了解一下`COUNT`的基本用法;
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -0,0 +1,114 @@
|
|||||||
|
---
|
||||||
|
title: 程序员最该拿的几种高含金量证书
|
||||||
|
category: 技术文章精选集
|
||||||
|
tag:
|
||||||
|
- 程序员
|
||||||
|
---
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
证书是能有效证明自己能力的好东西,它就是你实力的象征。在短短的面试时间内,证书可以为你加不少分。通过考证来提升自己,是一种性价比很高的办法。不过,相比金融、建筑、医疗等行业,IT 行业的职业资格证书并没有那么多。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
下面我总结了一下程序员可以考的一些常见证书。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 软考
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
全国计算机技术与软件专业技术资格(水平)考试,简称“软考”,是国内认可度较高的一项计算机技术资格认证。尽管一些人吐槽其实际价值,但在特定领域和情况下,它还是非常有用的,例如软考证书在国企和事业单位中具有较高的认可度、在某些城市软考证书可以用于积分落户、可用于个税补贴。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
软考有初、中、高三个级别,建议直接考高级。相比于PMP(项目管理专业人士认证),软考高项的难度更大,特别是论文部分,绝大部分人都挂在了论文部分。过了软考高项,在一些单位可以内部挂证,每个月多拿几百。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
官网地址:<https://www.ruankao.org.cn/>。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
备考建议:[2024年上半年,一次通过软考高级架构师考试的备考秘诀 - 阿里云开发者](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/9aUXHJ7dXgrHuT19jRhCnw)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## PAT
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
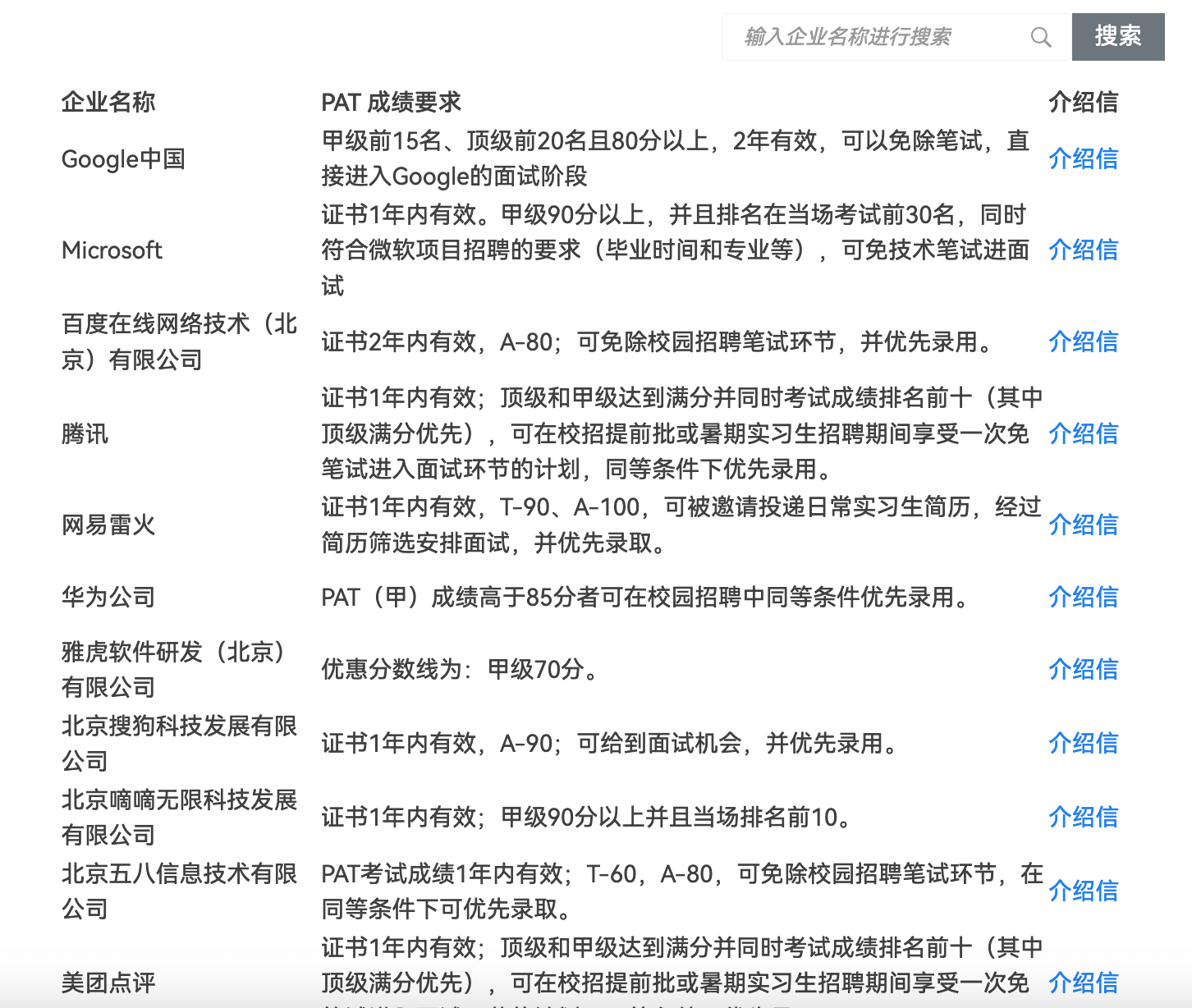
攀拓计算机能力测评(PAT)是一个专注于考察算法能力的测评体系,由浙江大学主办。该测评分为四个级别:基础级、乙级、甲级和顶级。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
通过PAT测评并达到联盟企业规定的相应评级和分数,可以跳过学历门槛,免除筛选简历和笔试环节,直接获得面试机会。具体有哪些公司可以去官网看看:<https://www.patest.cn/company> 。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
对于考研浙江大学的同学来说,PAT(甲级)成绩在一年内可以作为硕士研究生招生考试上机复试成绩。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## PMP
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
PMP(Project Management Professional)认证由美国项目管理协会(PMI)提供,是全球范围内认可度最高的项目管理专业人士资格认证。PMP认证旨在提升项目管理专业人士的知识和技能,确保项目顺利完成。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
PMP 是“一证在手,全球通用”的资格认证,对项目管理人士来说,PMP 证书含金量还是比较高的。放眼全球,很多成功企业都会将 PMP 认证作为项目经理的入职标准。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
但是!真正有价值的不是 PMP 证书,而是《PMBOK》 那套项目管理体系,在《PMBOK》(PMP 考试指定用书)中也包含了非常多商业活动、实业项目、组织规划、建筑行业等各个领域的项目案例。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
另外,PMP 证书不是一个高大上的证书,而是一个基础的证书。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## ACP
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
ACP(Agile Certified Practitioner)认证同样由美国项目管理协会(PMI)提供,是项目管理领域的另一个重要认证。与PMP(Project Management Professional)注重传统的瀑布方法论不同,ACP专注于敏捷项目管理方法论,如Scrum、Kanban、Lean、Extreme Programming(XP)等。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## OCP
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Oracle Certified Professional(OCP)是Oracle公司提供的一项专业认证,专注于Oracle数据库及相关技术。这个认证旨在验证和认证个人在使用和管理Oracle数据库方面的专业知识和技能。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
下图展示了 Oracle 认证的不同路径和相应的认证级别,分别是核心路径(Core Track)和专业路径(Speciality Track)。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 阿里云认证
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
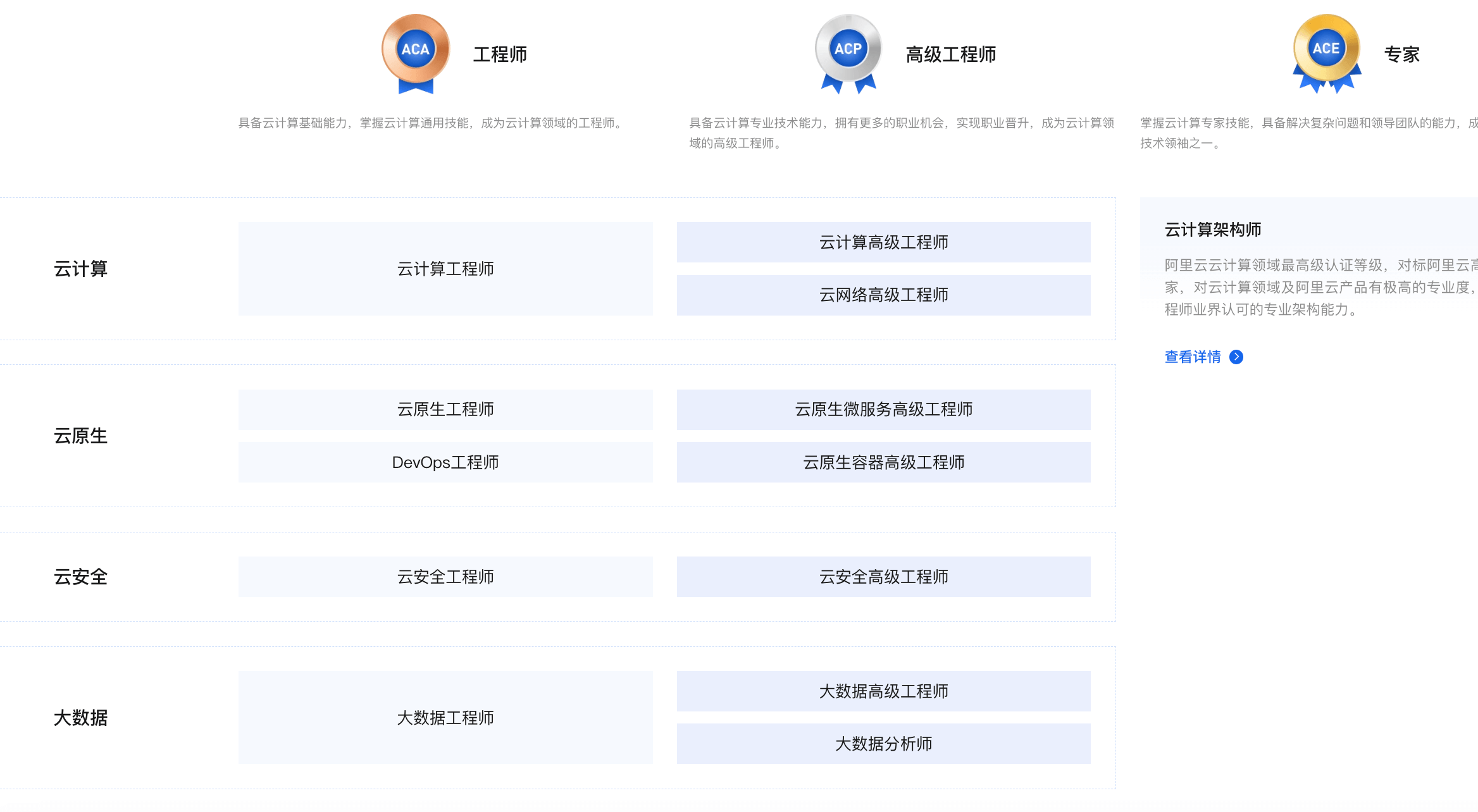
阿里云(Alibaba Cloud)提供的专业认证,认证方向包括云计算、大数据、人工智能、Devops等。职业认证分为 ACA、ACP、ACE 三个等级,除了职业认证之外,还有一个开发者Clouder认证,这是专门为开发者设立的专项技能认证。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
官网地址:<https://edu.aliyun.com/certification/>。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 华为认证
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
华为认证是由华为技术有限公司提供的面向ICT(信息与通信技术)领域的专业认证,认证方向包括网络、存储、云计算、大数据、人工智能等,非常庞大的认证体系。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## AWS 认证
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
AWS云认证考试是AWS云计算服务的官方认证考试,旨在验证IT专业人士在设计、部署和管理AWS基础架构方面的技能。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
AWS 认证分为多个级别,包括基础级、从业者级、助理级、专业级和专家级(Specialty),涵盖多个角色和技能:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **基础级别**:AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner,适合初学者,验证对 AWS 基础知识的理解,是最简单的入门认证。
|
||||||
|
- **助理级别**:包括 AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate、AWS Certified Developer – Associate 和 AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate,适合中级专业人士,验证其设计、开发和管理 AWS 应用的能力。
|
||||||
|
- **专业级别**:包括 AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Professional 和 AWS Certified DevOps Engineer – Professional,适合高级专业人士,验证其在复杂和大规模 AWS 环境中的能力。
|
||||||
|
- **专家级别**:包括 AWS Certified Advanced Networking – Specialty、AWS Certified Big Data – Specialty 等,专注于特定技术领域的深度知识和技能。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
备考建议:[小白入门云计算的最佳方式,是去考一张AWS的证书(附备考经验)](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/xAqNOnfZ05GDRuUbAiMHIA)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Google Cloud 认证
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
与 AWS 认证不同,Google Cloud 认证只有一门助理级认证(Associate Cloud Engineer),其他大部分为专业级(专家级)认证。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
备考建议:[如何备考谷歌云认证](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Vw5LGPI_akA7TQl1FMygWw)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
官网地址:<https://cloud.google.com/certification>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 微软认证
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
微软的认证体系主要针对其 Azure 云平台,分为基础级别、助理级别和专家级别,认证方向包括云计算、数据管理、开发、生产力工具等。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Elastic 认证
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Elastic 认证是由 Elastic 公司提供的一系列专业认证,旨在验证个人在使用 Elastic Stack(包括 Elasticsearch、Logstash、Kibana 、Beats 等)方面的技能和知识。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
如果你在日常开发核心工作是负责 ElasticSearch 相关业务的话,还是比较建议考的,含金量挺高。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
目前 Elastic 认证证书分为四类:Elastic Certified Engineer、Elastic Certified Analyst、Elastic Certified Observability Engineer、Elastic Certified SIEM Specialist。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
比较建议考 **Elastic Certified Engineer**,这个是 Elastic Stack 的基础认证,考察安装、配置、管理和维护 Elasticsearch 集群等核心技能。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## 其他
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- PostgreSQL 认证:国内的 PostgreSQL 认证分为专员级(PCA)、专家级(PCP)和大师级(PCM),主要考查 PostgreSQL 数据库管理和优化,价格略贵,不是很推荐。
|
||||||
|
- Kubernetes 认证:Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) 提供了几个官方认证,例如Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA)、Certified Kubernetes Application Developer (CKAD),主要考察Kubernetes 方面的技能和知识。
|
||||||
@ -23,6 +23,7 @@
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
## 程序员
|
## 程序员
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [程序员最该拿的几种高含金量证书](./programmer/high-value-certifications-for-programmers.md)
|
||||||
- [程序员怎样出版一本技术书](./programmer/how-do-programmers-publish-a-technical-book.md)
|
- [程序员怎样出版一本技术书](./programmer/how-do-programmers-publish-a-technical-book.md)
|
||||||
- [程序员高效出书避坑和实践指南](./programmer/efficient-book-publishing-and-practice-guide.md)
|
- [程序员高效出书避坑和实践指南](./programmer/efficient-book-publishing-and-practice-guide.md)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -18,14 +18,26 @@ head:
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
### 面向对象和面向过程的区别
|
### 面向对象和面向过程的区别
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
两者的主要区别在于解决问题的方式不同:
|
面向过程编程(Procedural-Oriented Programming,POP)和面向对象编程(Object-Oriented Programming,OOP)是两种常见的编程范式,两者的主要区别在于解决问题的方式不同:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- 面向过程把解决问题的过程拆成一个个方法,通过一个个方法的执行解决问题。
|
- **面向过程编程(POP)**:面向过程把解决问题的过程拆成一个个方法,通过一个个方法的执行解决问题。
|
||||||
- 面向对象会先抽象出对象,然后用对象执行方法的方式解决问题。
|
- **面向对象编程(OOP)**:面向对象会先抽象出对象,然后用对象执行方法的方式解决问题。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
另外,面向对象开发的程序一般更易维护、易复用、易扩展。
|
相比较于 POP,OOP 开发的程序一般具有下面这些优点:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
相关 issue : [面向过程:面向过程性能比面向对象高??](https://github.com/Snailclimb/JavaGuide/issues/431) 。
|
- **易维护**:由于良好的结构和封装性,OOP 程序通常更容易维护。
|
||||||
|
- **易复用**:通过继承和多态,OOP 设计使得代码更具复用性,方便扩展功能。
|
||||||
|
- **易扩展**:模块化设计使得系统扩展变得更加容易和灵活。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
POP 的编程方式通常更为简单和直接,适合处理一些较简单的任务。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
POP 和 OOP 的性能差异主要取决于它们的运行机制,而不仅仅是编程范式本身。因此,简单地比较两者的性能是一个常见的误区(相关 issue : [面向过程:面向过程性能比面向对象高??](https://github.com/Snailclimb/JavaGuide/issues/431) )。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在选择编程范式时,性能并不是唯一的考虑因素。代码的可维护性、可扩展性和开发效率同样重要。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
现代编程语言基本都支持多种编程范式,既可以用来进行面向过程编程,也可以进行面向对象编程。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
下面是一个求圆的面积和周长的示例,简单分别展示了面向对象和面向过程两种不同的解决方案。
|
下面是一个求圆的面积和周长的示例,简单分别展示了面向对象和面向过程两种不同的解决方案。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ tag:
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
`Atomic` 类依赖于 CAS(Compare-And-Swap,比较并交换)乐观锁来保证其方法的原子性,而不需要使用传统的锁机制(如 `synchronized` 块或 `ReentrantLock`)。
|
`Atomic` 类依赖于 CAS(Compare-And-Swap,比较并交换)乐观锁来保证其方法的原子性,而不需要使用传统的锁机制(如 `synchronized` 块或 `ReentrantLock`)。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
这篇文章我们直接介绍 Atomic 原子类的概念,具体实现原理可以阅读笔者写的这篇文章:[CAS 详解](./cas.md)。
|
这篇文章我们只介绍 Atomic 原子类的概念,具体实现原理可以阅读笔者写的这篇文章:[CAS 详解](./cas.md)。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -140,26 +140,55 @@ public final void lazySet(int i, int newValue)//最终 将index=i 位置的元
|
|||||||
**`AtomicIntegerArray` 类使用示例** :
|
**`AtomicIntegerArray` 类使用示例** :
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```java
|
```java
|
||||||
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicIntegerArray;
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
public class AtomicIntegerArrayTest {
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
|
||||||
int temvalue = 0;
|
|
||||||
int[] nums = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
|
int[] nums = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
|
||||||
AtomicIntegerArray i = new AtomicIntegerArray(nums);
|
// 创建 AtomicIntegerArray
|
||||||
|
AtomicIntegerArray atomicArray = new AtomicIntegerArray(nums);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// 打印 AtomicIntegerArray 中的初始值
|
||||||
|
System.out.println("Initial values in AtomicIntegerArray:");
|
||||||
for (int j = 0; j < nums.length; j++) {
|
for (int j = 0; j < nums.length; j++) {
|
||||||
System.out.println(i.get(j));
|
System.out.print("Index " + j + ": " + atomicArray.get(j) + " ");
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
temvalue = i.getAndSet(0, 2);
|
|
||||||
System.out.println("temvalue:" + temvalue + "; i:" + i);
|
|
||||||
temvalue = i.getAndIncrement(0);
|
|
||||||
System.out.println("temvalue:" + temvalue + "; i:" + i);
|
|
||||||
temvalue = i.getAndAdd(0, 5);
|
|
||||||
System.out.println("temvalue:" + temvalue + "; i:" + i);
|
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// 使用 getAndSet 方法将索引 0 处的值设置为 2,并返回旧值
|
||||||
|
int tempValue = atomicArray.getAndSet(0, 2);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println("\nAfter getAndSet(0, 2):");
|
||||||
|
System.out.println("Returned value: " + tempValue);
|
||||||
|
for (int j = 0; j < atomicArray.length(); j++) {
|
||||||
|
System.out.print("Index " + j + ": " + atomicArray.get(j) + " ");
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// 使用 getAndIncrement 方法将索引 0 处的值加 1,并返回旧值
|
||||||
|
tempValue = atomicArray.getAndIncrement(0);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println("\nAfter getAndIncrement(0):");
|
||||||
|
System.out.println("Returned value: " + tempValue);
|
||||||
|
for (int j = 0; j < atomicArray.length(); j++) {
|
||||||
|
System.out.print("Index " + j + ": " + atomicArray.get(j) + " ");
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// 使用 getAndAdd 方法将索引 0 处的值增加 5,并返回旧值
|
||||||
|
tempValue = atomicArray.getAndAdd(0, 5);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println("\nAfter getAndAdd(0, 5):");
|
||||||
|
System.out.println("Returned value: " + tempValue);
|
||||||
|
for (int j = 0; j < atomicArray.length(); j++) {
|
||||||
|
System.out.print("Index " + j + ": " + atomicArray.get(j) + " ");
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
输出:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```plain
|
||||||
|
Initial values in AtomicIntegerArray:
|
||||||
|
Index 0: 1 Index 1: 2 Index 2: 3 Index 3: 4 Index 4: 5 Index 5: 6
|
||||||
|
After getAndSet(0, 2):
|
||||||
|
Returned value: 1
|
||||||
|
Index 0: 2 Index 1: 2 Index 2: 3 Index 3: 4 Index 4: 5 Index 5: 6
|
||||||
|
After getAndIncrement(0):
|
||||||
|
Returned value: 2
|
||||||
|
Index 0: 3 Index 1: 2 Index 2: 3 Index 3: 4 Index 4: 5 Index 5: 6
|
||||||
|
After getAndAdd(0, 5):
|
||||||
|
Returned value: 3
|
||||||
|
Index 0: 8 Index 1: 2 Index 2: 3 Index 3: 4 Index 4: 5 Index 5: 6
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 引用类型原子类
|
## 引用类型原子类
|
||||||
@ -175,174 +204,133 @@ public class AtomicIntegerArrayTest {
|
|||||||
**`AtomicReference` 类使用示例** :
|
**`AtomicReference` 类使用示例** :
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```java
|
```java
|
||||||
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;
|
// Person 类
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
public class AtomicReferenceTest {
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
|
||||||
AtomicReference < Person > ar = new AtomicReference < Person > ();
|
|
||||||
Person person = new Person("SnailClimb", 22);
|
|
||||||
ar.set(person);
|
|
||||||
Person updatePerson = new Person("Daisy", 20);
|
|
||||||
ar.compareAndSet(person, updatePerson);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
System.out.println(ar.get().getName());
|
|
||||||
System.out.println(ar.get().getAge());
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
class Person {
|
class Person {
|
||||||
private String name;
|
private String name;
|
||||||
private int age;
|
private int age;
|
||||||
|
//省略getter/setter和toString
|
||||||
public Person(String name, int age) {
|
|
||||||
super();
|
|
||||||
this.name = name;
|
|
||||||
this.age = age;
|
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
public String getName() {
|
|
||||||
return name;
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
public void setName(String name) {
|
// 创建 AtomicReference 对象并设置初始值
|
||||||
this.name = name;
|
AtomicReference<Person> ar = new AtomicReference<>(new Person("SnailClimb", 22));
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
public int getAge() {
|
// 打印初始值
|
||||||
return age;
|
System.out.println("Initial Person: " + ar.get().toString());
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
public void setAge(int age) {
|
// 更新值
|
||||||
this.age = age;
|
Person updatePerson = new Person("Daisy", 20);
|
||||||
}
|
ar.compareAndSet(ar.get(), updatePerson);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
}
|
// 打印更新后的值
|
||||||
|
System.out.println("Updated Person: " + ar.get().toString());
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// 尝试再次更新
|
||||||
|
Person anotherUpdatePerson = new Person("John", 30);
|
||||||
|
boolean isUpdated = ar.compareAndSet(updatePerson, anotherUpdatePerson);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// 打印是否更新成功及最终值
|
||||||
|
System.out.println("Second Update Success: " + isUpdated);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println("Final Person: " + ar.get().toString());
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
上述代码首先创建了一个 `Person` 对象,然后把 `Person` 对象设置进 `AtomicReference` 对象中,然后调用 `compareAndSet` 方法,该方法就是通过 CAS 操作设置 ar。如果 ar 的值为 `person` 的话,则将其设置为 `updatePerson`。实现原理与 `AtomicInteger` 类中的 `compareAndSet` 方法相同。运行上面的代码后的输出结果如下:
|
输出:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```plain
|
```plain
|
||||||
Daisy
|
Initial Person: Person{name='SnailClimb', age=22}
|
||||||
20
|
Updated Person: Person{name='Daisy', age=20}
|
||||||
|
Second Update Success: true
|
||||||
|
Final Person: Person{name='John', age=30}
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**`AtomicStampedReference` 类使用示例** :
|
**`AtomicStampedReference` 类使用示例** :
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```java
|
```java
|
||||||
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicStampedReference;
|
// 创建一个 AtomicStampedReference 对象,初始值为 "SnailClimb",初始版本号为 1
|
||||||
|
AtomicStampedReference<String> asr = new AtomicStampedReference<>("SnailClimb", 1);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
public class AtomicStampedReferenceDemo {
|
// 打印初始值和版本号
|
||||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
int[] initialStamp = new int[1];
|
||||||
// 实例化、取当前值和 stamp 值
|
String initialRef = asr.get(initialStamp);
|
||||||
final Integer initialRef = 0, initialStamp = 0;
|
System.out.println("Initial Reference: " + initialRef + ", Initial Stamp: " + initialStamp[0]);
|
||||||
final AtomicStampedReference<Integer> asr = new AtomicStampedReference<>(initialRef, initialStamp);
|
|
||||||
System.out.println("currentValue=" + asr.getReference() + ", currentStamp=" + asr.getStamp());
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// compare and set
|
// 更新值和版本号
|
||||||
final Integer newReference = 666, newStamp = 999;
|
int oldStamp = initialStamp[0];
|
||||||
final boolean casResult = asr.compareAndSet(initialRef, newReference, initialStamp, newStamp);
|
String oldRef = initialRef;
|
||||||
System.out.println("currentValue=" + asr.getReference()
|
String newRef = "Daisy";
|
||||||
+ ", currentStamp=" + asr.getStamp()
|
int newStamp = oldStamp + 1;
|
||||||
+ ", casResult=" + casResult);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 获取当前的值和当前的 stamp 值
|
boolean isUpdated = asr.compareAndSet(oldRef, newRef, oldStamp, newStamp);
|
||||||
int[] arr = new int[1];
|
System.out.println("Update Success: " + isUpdated);
|
||||||
final Integer currentValue = asr.get(arr);
|
|
||||||
final int currentStamp = arr[0];
|
|
||||||
System.out.println("currentValue=" + currentValue + ", currentStamp=" + currentStamp);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 单独设置 stamp 值
|
// 打印更新后的值和版本号
|
||||||
final boolean attemptStampResult = asr.attemptStamp(newReference, 88);
|
int[] updatedStamp = new int[1];
|
||||||
System.out.println("currentValue=" + asr.getReference()
|
String updatedRef = asr.get(updatedStamp);
|
||||||
+ ", currentStamp=" + asr.getStamp()
|
System.out.println("Updated Reference: " + updatedRef + ", Updated Stamp: " + updatedStamp[0]);
|
||||||
+ ", attemptStampResult=" + attemptStampResult);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 重新设置当前值和 stamp 值
|
// 尝试用错误的版本号更新
|
||||||
asr.set(initialRef, initialStamp);
|
boolean isUpdatedWithWrongStamp = asr.compareAndSet(newRef, "John", oldStamp, newStamp + 1);
|
||||||
System.out.println("currentValue=" + asr.getReference() + ", currentStamp=" + asr.getStamp());
|
System.out.println("Update with Wrong Stamp Success: " + isUpdatedWithWrongStamp);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// [不推荐使用,除非搞清楚注释的意思了] weak compare and set
|
// 打印最终的值和版本号
|
||||||
// 困惑!weakCompareAndSet 这个方法最终还是调用 compareAndSet 方法。[版本: jdk-8u191]
|
int[] finalStamp = new int[1];
|
||||||
// 但是注释上写着 "May fail spuriously and does not provide ordering guarantees,
|
String finalRef = asr.get(finalStamp);
|
||||||
// so is only rarely an appropriate alternative to compareAndSet."
|
System.out.println("Final Reference: " + finalRef + ", Final Stamp: " + finalStamp[0]);
|
||||||
// todo 感觉有可能是 jvm 通过方法名在 native 方法里面做了转发
|
|
||||||
final boolean wCasResult = asr.weakCompareAndSet(initialRef, newReference, initialStamp, newStamp);
|
|
||||||
System.out.println("currentValue=" + asr.getReference()
|
|
||||||
+ ", currentStamp=" + asr.getStamp()
|
|
||||||
+ ", wCasResult=" + wCasResult);
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
输出结果如下:
|
输出结果如下:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```plain
|
```plain
|
||||||
currentValue=0, currentStamp=0
|
Initial Reference: SnailClimb, Initial Stamp: 1
|
||||||
currentValue=666, currentStamp=999, casResult=true
|
Update Success: true
|
||||||
currentValue=666, currentStamp=999
|
Updated Reference: Daisy, Updated Stamp: 2
|
||||||
currentValue=666, currentStamp=88, attemptStampResult=true
|
Update with Wrong Stamp Success: false
|
||||||
currentValue=0, currentStamp=0
|
Final Reference: Daisy, Final Stamp: 2
|
||||||
currentValue=666, currentStamp=999, wCasResult=true
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**`AtomicMarkableReference` 类使用示例** :
|
**`AtomicMarkableReference` 类使用示例** :
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```java
|
```java
|
||||||
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicMarkableReference;
|
// 创建一个 AtomicMarkableReference 对象,初始值为 "SnailClimb",初始标记为 false
|
||||||
|
AtomicMarkableReference<String> amr = new AtomicMarkableReference<>("SnailClimb", false);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
public class AtomicMarkableReferenceDemo {
|
// 打印初始值和标记
|
||||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
boolean[] initialMark = new boolean[1];
|
||||||
// 实例化、取当前值和 mark 值
|
String initialRef = amr.get(initialMark);
|
||||||
final Boolean initialRef = null, initialMark = false;
|
System.out.println("Initial Reference: " + initialRef + ", Initial Mark: " + initialMark[0]);
|
||||||
final AtomicMarkableReference<Boolean> amr = new AtomicMarkableReference<>(initialRef, initialMark);
|
|
||||||
System.out.println("currentValue=" + amr.getReference() + ", currentMark=" + amr.isMarked());
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// compare and set
|
// 更新值和标记
|
||||||
final Boolean newReference1 = true, newMark1 = true;
|
String oldRef = initialRef;
|
||||||
final boolean casResult = amr.compareAndSet(initialRef, newReference1, initialMark, newMark1);
|
String newRef = "Daisy";
|
||||||
System.out.println("currentValue=" + amr.getReference()
|
boolean oldMark = initialMark[0];
|
||||||
+ ", currentMark=" + amr.isMarked()
|
boolean newMark = true;
|
||||||
+ ", casResult=" + casResult);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 获取当前的值和当前的 mark 值
|
boolean isUpdated = amr.compareAndSet(oldRef, newRef, oldMark, newMark);
|
||||||
boolean[] arr = new boolean[1];
|
System.out.println("Update Success: " + isUpdated);
|
||||||
final Boolean currentValue = amr.get(arr);
|
|
||||||
final boolean currentMark = arr[0];
|
|
||||||
System.out.println("currentValue=" + currentValue + ", currentMark=" + currentMark);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 单独设置 mark 值
|
// 打印更新后的值和标记
|
||||||
final boolean attemptMarkResult = amr.attemptMark(newReference1, false);
|
boolean[] updatedMark = new boolean[1];
|
||||||
System.out.println("currentValue=" + amr.getReference()
|
String updatedRef = amr.get(updatedMark);
|
||||||
+ ", currentMark=" + amr.isMarked()
|
System.out.println("Updated Reference: " + updatedRef + ", Updated Mark: " + updatedMark[0]);
|
||||||
+ ", attemptMarkResult=" + attemptMarkResult);
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// 重新设置当前值和 mark 值
|
// 尝试用错误的标记更新
|
||||||
amr.set(initialRef, initialMark);
|
boolean isUpdatedWithWrongMark = amr.compareAndSet(newRef, "John", oldMark, !newMark);
|
||||||
System.out.println("currentValue=" + amr.getReference() + ", currentMark=" + amr.isMarked());
|
System.out.println("Update with Wrong Mark Success: " + isUpdatedWithWrongMark);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
// [不推荐使用,除非搞清楚注释的意思了] weak compare and set
|
// 打印最终的值和标记
|
||||||
// 困惑!weakCompareAndSet 这个方法最终还是调用 compareAndSet 方法。[版本: jdk-8u191]
|
boolean[] finalMark = new boolean[1];
|
||||||
// 但是注释上写着 "May fail spuriously and does not provide ordering guarantees,
|
String finalRef = amr.get(finalMark);
|
||||||
// so is only rarely an appropriate alternative to compareAndSet."
|
System.out.println("Final Reference: " + finalRef + ", Final Mark: " + finalMark[0]);
|
||||||
// todo 感觉有可能是 jvm 通过方法名在 native 方法里面做了转发
|
|
||||||
final boolean wCasResult = amr.weakCompareAndSet(initialRef, newReference1, initialMark, newMark1);
|
|
||||||
System.out.println("currentValue=" + amr.getReference()
|
|
||||||
+ ", currentMark=" + amr.isMarked()
|
|
||||||
+ ", wCasResult=" + wCasResult);
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
输出结果如下:
|
输出结果如下:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```plain
|
```plain
|
||||||
currentValue=null, currentMark=false
|
Initial Reference: SnailClimb, Initial Mark: false
|
||||||
currentValue=true, currentMark=true, casResult=true
|
Update Success: true
|
||||||
currentValue=true, currentMark=true
|
Updated Reference: Daisy, Updated Mark: true
|
||||||
currentValue=true, currentMark=false, attemptMarkResult=true
|
Update with Wrong Mark Success: false
|
||||||
currentValue=null, currentMark=false
|
Final Reference: Daisy, Final Mark: true
|
||||||
currentValue=true, currentMark=true, wCasResult=true
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 对象的属性修改类型原子类
|
## 对象的属性修改类型原子类
|
||||||
@ -360,52 +348,48 @@ currentValue=true, currentMark=true, wCasResult=true
|
|||||||
**`AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater` 类使用示例** :
|
**`AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater` 类使用示例** :
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```java
|
```java
|
||||||
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater;
|
// Person 类
|
||||||
|
class Person {
|
||||||
public class AtomicIntegerFieldUpdaterTest {
|
|
||||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
|
||||||
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<User> a = AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(User.class, "age");
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
User user = new User("Java", 22);
|
|
||||||
System.out.println(a.getAndIncrement(user));// 22
|
|
||||||
System.out.println(a.get(user));// 23
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
class User {
|
|
||||||
private String name;
|
private String name;
|
||||||
public volatile int age;
|
// 要使用 AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater,字段必须是 public volatile
|
||||||
|
private volatile int age;
|
||||||
public User(String name, int age) {
|
//省略getter/setter和toString
|
||||||
super();
|
|
||||||
this.name = name;
|
|
||||||
this.age = age;
|
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
public String getName() {
|
// 创建 AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater 对象
|
||||||
return name;
|
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<Person> ageUpdater = AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(Person.class, "age");
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
public void setName(String name) {
|
// 创建 Person 对象
|
||||||
this.name = name;
|
Person person = new Person("SnailClimb", 22);
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
public int getAge() {
|
// 打印初始值
|
||||||
return age;
|
System.out.println("Initial Person: " + person);
|
||||||
}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
public void setAge(int age) {
|
// 更新 age 字段
|
||||||
this.age = age;
|
ageUpdater.incrementAndGet(person); // 自增
|
||||||
}
|
System.out.println("After Increment: " + person);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
}
|
ageUpdater.addAndGet(person, 5); // 增加 5
|
||||||
|
System.out.println("After Adding 5: " + person);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
ageUpdater.compareAndSet(person, 28, 30); // 如果当前值是 28,则设置为 30
|
||||||
|
System.out.println("After Compare and Set (28 to 30): " + person);
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
// 尝试使用错误的比较值进行更新
|
||||||
|
boolean isUpdated = ageUpdater.compareAndSet(person, 28, 35); // 这次应该失败
|
||||||
|
System.out.println("Compare and Set (28 to 35) Success: " + isUpdated);
|
||||||
|
System.out.println("Final Person: " + person);
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
输出结果:
|
输出结果:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```plain
|
```plain
|
||||||
22
|
Initial Person: Name: SnailClimb, Age: 22
|
||||||
23
|
After Increment: Name: SnailClimb, Age: 23
|
||||||
|
After Adding 5: Name: SnailClimb, Age: 28
|
||||||
|
After Compare and Set (28 to 30): Name: SnailClimb, Age: 30
|
||||||
|
Compare and Set (28 to 35) Success: false
|
||||||
|
Final Person: Name: SnailClimb, Age: 30
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## 参考
|
## 参考
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -40,14 +40,18 @@ boolean compareAndSwapInt(Object o, long offset, int expected, int x);
|
|||||||
boolean compareAndSwapLong(Object o, long offset, long expected, long x);
|
boolean compareAndSwapLong(Object o, long offset, long expected, long x);
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`Unsafe`类中的 CAS 方法是`native`方法。`native`关键字表明这些方法是用本地代码(通常是 C 或 C++)实现的,而不是用 Java 实现的。这些方法直接调用底层的硬件指令来实现原子操作。也就是说,Java 语言并没有直接用 Java 实现 CAS,而是通过 C++ 内联汇编的形式实现的(通过 JNI 调用)。因此,CAS 的具体实现与操作系统以及 CPU 密切相关。
|
`Unsafe`类中的 CAS 方法是`native`方法。`native`关键字表明这些方法是用本地代码(通常是 C 或 C++)实现的,而不是用 Java 实现的。这些方法直接调用底层的硬件指令来实现原子操作。也就是说,Java 语言并没有直接用 Java 实现 CAS。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`java.util.concurrent.atomic` 包提供了一些用于原子操作的类。这些类利用底层的原子指令,确保在多线程环境下的操作是线程安全的。
|
更准确点来说,Java 中 CAS 是 C++ 内联汇编的形式实现的,通过 JNI(Java Native Interface) 调用。因此,CAS 的具体实现与操作系统以及 CPU 密切相关。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`java.util.concurrent.atomic` 包提供了一些用于原子操作的类。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||

|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
关于这些 Atomic 原子类的介绍和使用,可以阅读这篇文章:[Atomic 原子类总结](https://javaguide.cn/java/concurrent/atomic-classes.html)。
|
关于这些 Atomic 原子类的介绍和使用,可以阅读这篇文章:[Atomic 原子类总结](https://javaguide.cn/java/concurrent/atomic-classes.html)。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Atomic 类依赖于 CAS 乐观锁来保证其方法的原子性,而不需要使用传统的锁机制(如 `synchronized` 块或 `ReentrantLock`)。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
`AtomicInteger`是 Java 的原子类之一,主要用于对 `int` 类型的变量进行原子操作,它利用`Unsafe`类提供的低级别原子操作方法实现无锁的线程安全性。
|
`AtomicInteger`是 Java 的原子类之一,主要用于对 `int` 类型的变量进行原子操作,它利用`Unsafe`类提供的低级别原子操作方法实现无锁的线程安全性。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
下面,我们通过解读`AtomicInteger`的核心源码(JDK1.8),来说明 Java 如何使用`Unsafe`类的方法来实现原子操作。
|
下面,我们通过解读`AtomicInteger`的核心源码(JDK1.8),来说明 Java 如何使用`Unsafe`类的方法来实现原子操作。
|
||||||
@ -147,8 +151,6 @@ CAS 经常会用到自旋操作来进行重试,也就是不成功就一直循
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
### 只能保证一个共享变量的原子操作
|
### 只能保证一个共享变量的原子操作
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
CAS 只对单个共享变量有效,当操作涉及跨多个共享变量时 CAS 无效。但是从 JDK 1.5 开始,提供了`AtomicReference`类来保证引用对象之间的原子性,你可以把多个变量放在一个对象里来进行 CAS 操作.所以我们可以使用锁或者利用`AtomicReference`类把多个共享变量合并成一个共享变量来操作。
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
CAS 操作仅能对单个共享变量有效。当需要操作多个共享变量时,CAS 就显得无能为力。不过,从 JDK 1.5 开始,Java 提供了`AtomicReference`类,这使得我们能够保证引用对象之间的原子性。通过将多个变量封装在一个对象中,我们可以使用`AtomicReference`来执行 CAS 操作。
|
CAS 操作仅能对单个共享变量有效。当需要操作多个共享变量时,CAS 就显得无能为力。不过,从 JDK 1.5 开始,Java 提供了`AtomicReference`类,这使得我们能够保证引用对象之间的原子性。通过将多个变量封装在一个对象中,我们可以使用`AtomicReference`来执行 CAS 操作。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
除了 `AtomicReference` 这种方式之外,还可以利用加锁来保证。
|
除了 `AtomicReference` 这种方式之外,还可以利用加锁来保证。
|
||||||
@ -157,4 +159,4 @@ CAS 操作仅能对单个共享变量有效。当需要操作多个共享变量
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
在 Java 中,CAS 通过 `Unsafe` 类中的 `native` 方法实现,这些方法调用底层的硬件指令来完成原子操作。由于其实现依赖于 C++ 内联汇编和 JNI 调用,因此 CAS 的具体实现与操作系统以及 CPU 密切相关。
|
在 Java 中,CAS 通过 `Unsafe` 类中的 `native` 方法实现,这些方法调用底层的硬件指令来完成原子操作。由于其实现依赖于 C++ 内联汇编和 JNI 调用,因此 CAS 的具体实现与操作系统以及 CPU 密切相关。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
CAS 作为实现乐观锁的核心算法,虽然具有高效的无锁特性,但也需要注意 ABA 问题、循环时间长开销大等问题。
|
CAS 虽然具有高效的无锁特性,但也需要注意 ABA 、循环时间长开销大等问题。
|
||||||
|
|||||||
Loading…
x
Reference in New Issue
Block a user